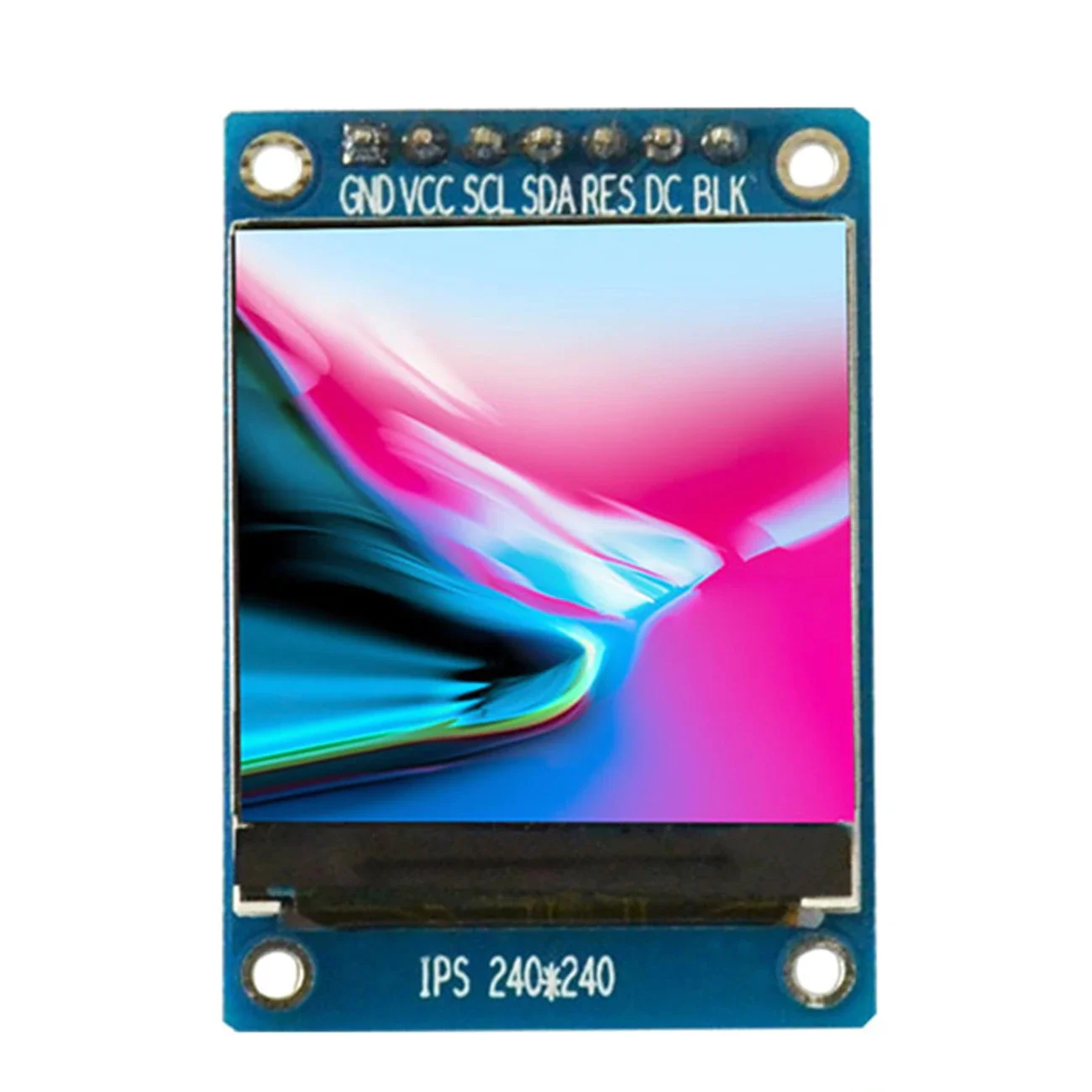
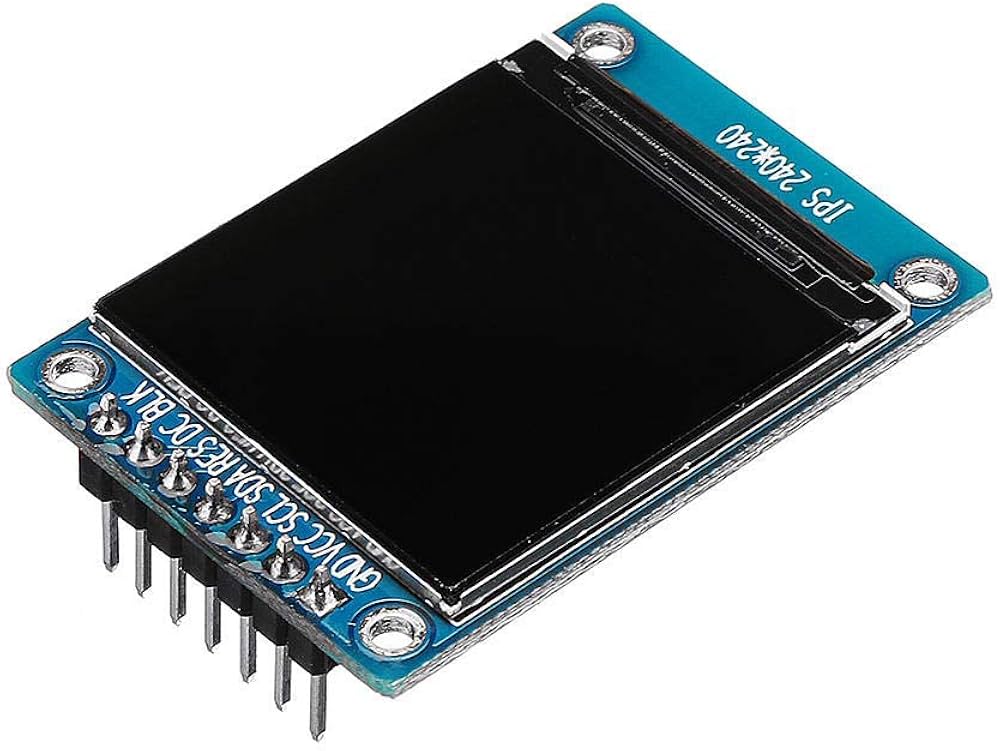
1.3 inch IPS HD TFT ST7789 Drive IC 240*240 SPI
₵85.00
The 1.3 inch ST7789 Display is a high-definition IPS module that brings vibrant colors to your compact projects. With a sharp 240×240 resolution and fast SPI interface, it is significantly clearer and faster than standard OLED screens.
Voltage Warning: This display operates on 3.3V Logic. If you are using a 5V Arduino Uno, you MUST use resistors or a Logic Level Converter on the data pins (SDA, SCK, RES, DC), or you risk damaging the screen.
2 in stock
Product Overview
This display module offers excellent visual quality in a compact format, making it ideal for wearables, portable devices, and micro-controller projects (like those using Arduino or ESP32).
Key Components
| Component | Specification | Description |
| Size | 1.3 inches (Diagonal) | Compact size suitable for wearables and handheld devices. |
| Display Type | IPS TFT (In-Plane Switching Thin-Film Transistor) | Provides superior color accuracy and ultra-wide viewing angles compared to older TN (Twisted Nematic) TFT technology. |
| Resolution | $240 \times 240$ | A high-definition (HD) square resolution for its small size, resulting in a crisp image and good pixel-per-inch (PPI) density. |
| Driver IC | ST7789 | The integrated circuit is responsible for controlling the display’s pixels. It handles data processing, memory, and timing signals. |
| Interface | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) | The communication protocol used to send display data (commands and pixel data) to the driver IC. |
The ST7789 Driver IC
The ST7789 is a single-chip controller/driver for a 240 \times 320 dot graphic display, though it’s commonly used here to drive the 240 \times 240 display area.
- Function: It features an internal power supply circuit, oscillator, and a controller that manages the display’s source and gate drivers.
- Color Depth: The driver typically supports up to 262k colors (18-bit), though it is often used with 65K colors (16-bit) in microcontroller applications to save memory and processing time.
- Memory: The IC includes internal GRAM (Graphic RAM) where the pixel data is stored before being displayed.
SPI Communication Interface
The use of the SPI interface is a major advantage for small microcontrollers. SPI is a synchronous serial data link standard that operates in full duplex mode.
Common Pins
The module typically exposes 7 to 8 pins, which include power and the necessary SPI lines:
| Pin Name | Full Name | Function | Note |
| VCC/VDD | Power Supply | Typically 3.3V (It’s essential to check the specific module’s datasheet). | |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection. | |
| SCK | Serial Clock | Clock signal line. | Required for data synchronization. |
| SDA/MOSI | Master Out Slave In | Data line from the microcontroller (Master) to the display (Slave). | |
| RES | Reset | Used to hardware reset the ST7789 driver. | Needs to be toggled low briefly during initialization. |
| DC | Data/Command | Used to tell the driver IC whether the data being sent on SDA} is a Command (DC rightarrow LOW) or Pixel Data (DC rightarrow HIGH). | |
| CS | Chip Select | Used to enable/disable the display module. | Usually held LOW if it’s the only SPI device. |
| BLK | Backlight Control | Controls the LED backlight (often active HIGH). | Can be connected to a PWM pin for brightness control. |
Benefits of SPI
- High Speed: SPI can transmit data quickly, allowing for fast screen refreshes and smooth graphics.
- Low Pin Count: Uses fewer microcontroller pins (typically 4-5) compared to parallel interfaces, saving I/O for other sensors and functions.
Applications
This display is extremely popular in projects requiring a high-quality visual output in a small space:
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- Portable Instruments: Small digital multimeters or logging devices.
- Embedded HMI (Human-Machine Interface): Status panels for home automation or industrial controllers.
- IoT Devices: Displaying sensor data, network status, or time.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.