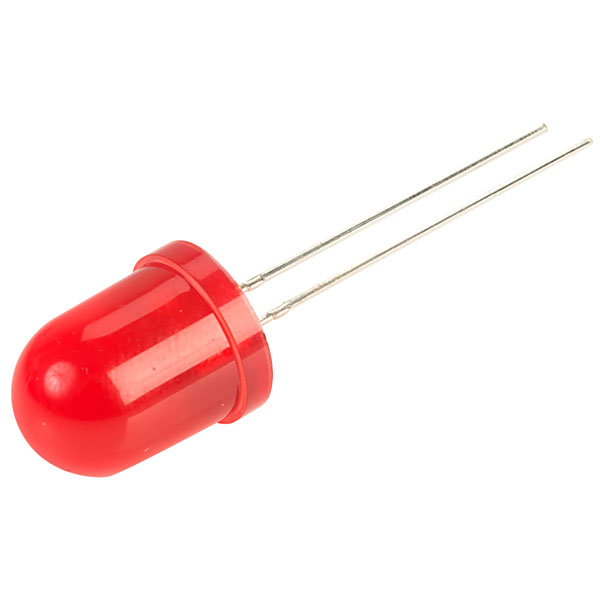
Red LED (Light Emitting Diode)
₵0.50
A Red LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a type of semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. It is one of the most common electronic components, used primarily as an indicator light.
1000 in stock
Fundamentals of Red LEDs
Color and Wavelength
The color of an LED is determined by the semiconductor material used in the diode.
- Material: Red LEDs commonly use materials like Gallium Arsenide Phosphide ($\text{GaAsP}$) or Aluminum Gallium Arsenide ($\text{AlGaAs}$).
- Wavelength: Red light typically has a wavelength in the range of 620 to 750 nanometers (nm).
How it Works (Electroluminescence)
- An LED is a PN-junction diode.
- When a forward voltage is applied (the positive lead, or anode, is connected to the positive terminal, and the negative lead, or cathode, is connected to the negative terminal), electrons move across the junction.
- In the P-type material, these electrons recombine with holes (the absence of an electron).
- As the electrons drop from a higher energy level to a lower one, they release energy in the form of photons (light). This phenomenon is called electroluminescence. The energy drop is small, resulting in the long wavelength of red light.
Electrical Characteristics
To prevent damage, an LED must always be used with a current-limiting resistor when connected to a voltage source greater than its forward voltage.
| Characteristic | Typical Value (Red LED) |
| Forward Voltage ($\text{V}_f$) | $\approx 1.8 \text{V}$ to $2.2 \text{V}$ |
| Forward Current ($\text{I}_f$) | $\approx 10 \text{mA}$ to $20 \text{mA}$ (Standard) |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage ($\text{V}_{r,max}$) | $\approx 5 \text{V}$ (Do not connect backward to high voltage) |
Calculating the Resistor Value
The required resistance ($R$) is calculated using Ohm’s Law:
- $V_{supply}$: The voltage of your power source (e.g., 5V from an Arduino).
- $V_f$: The LED’s forward voltage (e.g., 2.0V).
- $I_f$: The desired forward current (e.g., 0.020A or 20mA).
Example: Using a 5V supply, a 2.0V LED, and targeting 20mA:
You would typically use the nearest standard resistor value, such as $150 \Omega$ or $220 \Omega$.
Identification and Polarity
It’s crucial to connect an LED with the correct polarity (forward-biased).
- Anode (Positive): This is the longer lead of a new LED, and the connection inside the LED has the smaller plate.
- Cathode (Negative): This is the shorter lead, and the plastic casing often has a flat edge on this side. The connection inside has the larger plate (the base).



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.